Prostatitis is an inflammation of a person's prostate gland.The prostate is located just below the bladder and chestnut size.It surrounds the first part of the urethra and extends to the installed pelvic floor, consisting of muscle.
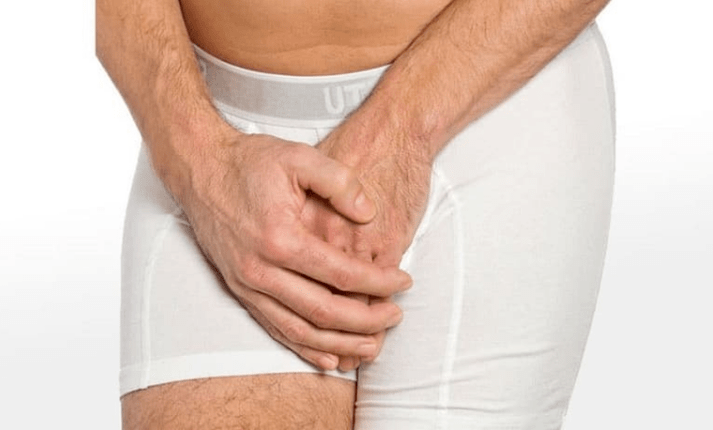
Prostate produces secretion, which includes PSA and sperm.PSA makes the ejaculation more liquid.Sperm is important for sperm mobility.
Prostatitis is mainly associated with severe pain in the perineum and anal region.In addition, symptoms such as urinary frequency, urinary tract pain and pain during ejaculation occur during prostate inflammation.
Prostate is often affected by inflammation.The probability of prostate infection increases with age.Studies show that most cases are 40 to 50 years old.
Prostatitis syndrome
At the same time, the expanded understanding of the term prostatitis appears in medicine.With coordinated prostatitis syndrome, several complaints are summarized in the human pelvic area, which usually has unknown reasons.The term "prostatitis syndrome" summarizes various clinical drawings:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Chronic bacterial prostatitis
- Inflammatory syndrome instead of inflammation of chronic pelvic pain
- Prostatitis without symptoms
Acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis
Acute prostatitis is caused by bacteria.Bacteria either through blood to the prostate, or spread from bladder or urethra bacterial infections to the prostate.Acute prostatitis is usually a serious common condition with severe pain during urination, fever and chills.
Chronic prostatitis can develop from acute: if for more than three months there is inflammation of the prostate gland and recurrent microbes in the urine, prostate expression or ejaculation, then this is a chronic inflammation.
Bacterial prostatitis.This is less flashing than acute prostatitis.Although chronic inflammation of the prostate gland causes pain during urination and, possibly, the feeling of pressure in the perineum, but complaints are usually not as described as acute prostatitis.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (abakteral prostatitis)
In most cases, prostate infections, bacteria cannot be detected in the urine, prostate or ejaculation as the cause of the disease.The trigger of prostatitis is still unclear.The doctor mentioned that he had chronic pelvic pain.
However, in such cases, leukocytes are often detected as an expression of inflammation in the prostate gland.To distinguish this, another form of disease in which bacteria or leukocytes are not detected.Chronic pelvic pain syndrome is the most common form of prostatitis.
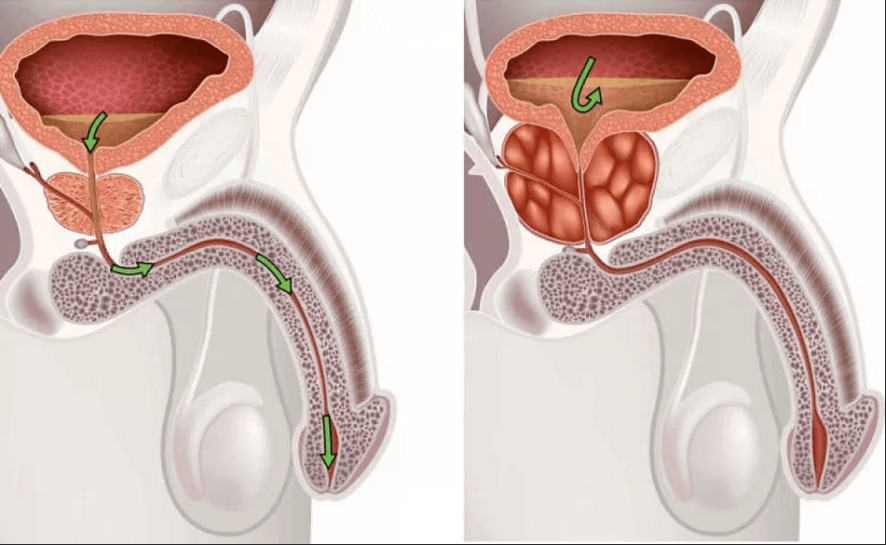
Prostatitis without symptoms
In rare cases, asymptomatic prostatitis occurs.With this form of prostatitis, although there are signs of inflammation, but there is no other pain or symptoms.Prostatitis without symptoms is usually detected by accident, for example, as part of the study of infertility.
Prostatitis: Symptoms
Prostate inflammation can cause a variety of symptoms of prostatitis.Although the symptoms of acute prostatitis can be very serious and cause strong anger, with chronic prostatitis they are usually relatively weak.
Acute prostatitis: Symptoms
Acute prostatitis is often an acute disease in which the patient has a fever and chills.Abandonment causes burning pain, and urine flow is reduced due to prostate gland edema.Because the victim can distinguish only a small amount of urine, they have a constant urination and often go to the toilet.Symptoms of other prostatitis symptoms include bladder, pelvic pain and back pain.Pain can also occur during or after ejaculation.
Chronic prostatitis: Symptoms
Prostatitis with chronic courses usually causes less serious symptoms than acute inflammation of the prostate.Symptoms such as fever and chills are usually absent.Symptoms, such as the feeling of pressure in the perineum or lower abdomen, the darkness of ejaculation due to blood in sperm or blood in the urine is typical for chronic inflammation of the prostate. Symptoms of chronic and chronic bacterial prostatitis are no different.
Complications of prostatitis
The most common complication is prostate abscess.Prostate gland abscesses are purulent inflammation of the inflammation, which usually needs to be opened and empty with cuts.
As further complications of prostate inflammation, inflammation can be used for nearby structures, such as testis or penis attachments.There is also suspicion that chronic prostatitis is associated with the development of prostate cancer.
Prostatitis: Causes and Risk Factors
Bacterial prostatitis: Causes
Only ten percent of cases of prostatitis are caused by prostate bacteria.Bacteria can enter the prostate through the blood or from neighboring organs, such as the bladder or urethra, where they can lead to the reaction of the inflammation.
Bacteria escherichia coli, mostly found in the human intestine, is the most common cause of prostatitis.Klebsiella, enterococci or mycobacteria can also cause prostatitis.Bacterial prostatitis can also be caused by sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia or trichomonas, as well as gonorrhea.
In chronic prostatitis, bacteria in the prostate gland avoid unexplained methods to protect the human immune system.This allows microbes to always colonize the prostate.Antibiotics are relatively poor in prostate gland tissue, which can be another cause of bacterial survival in the prostate gland.
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome: Causes
The true cause of chronic pelvic pain syndrome has not been fully studied.Scientists have nominated many theories, each of which sounds reasonable, but everything has not been clearly proven.In some cases, the genetic material of the unknown microorganism was previously found in the pelvis.Therefore, the cause of the pelvic pain syndrome may be microorganisms that are still unable to grow in the laboratory and, therefore, are not detected.
Another possible cause of chronic pelvic pain is bladder disorders.As drainage is affected, the number of bladder increases, thus suppressing the prostate.These pressure eventually damage the prostate gland tissue, causing inflammation.
However, in many cases, the cause of chronic pelvic pain cannot be clearly shown.Then the doctor talks about idiopathic prostatitis.
The reason anatomy
In rare cases, prostatitis is caused by narrowing of the urinary tract.If the urinary tract is narrow, the urine accumulates and, if it enters the prostate, it can also cause inflammation.This narrowing can be caused by a tumor or stone -the prostate stone installed.
Mental excuse
Recently, more and more causes of prostatitis have been discussed.In particular, with non -inflammatory syndrome chronic pelvic pain, mental trigger is possible.The right mechanism is still unknown.
Risk factors for the development of prostatitis
Some men are mainly at risk for developing prostate infections.This includes, for example, men who violate the immune system or oppressed by the immune system.In addition, major diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, can contribute to the development of prostatitis: increased blood sugar levels in diabetic patients often cause increased sugar in urine.Excessive sugar content in the urine can provide bacteria with good growth conditions, facilitating the development of urinary tract infections.
Another risk factor in the development of prostatitis is the bladder coat.The introduction of a catheter through the urethra through the urethra can cause a small rupture of the urethra and damage the prostate gland.In addition, such as foreign bodies, bacteria can settle in the bladder and form a biofilm formed.As a result, bacteria can rise along the urethra to the bladder, leading to prostate infection.
Prostatitis: examination and diagnostics
A general practitioner may take medical history, but if there is suspicion of prostatitis, he or she will direct you to a urologist.This does a physical examination.If suspected of prostatitis, this is usually a digital rectal study called.However, this study does not provide clear evidence of prostate inflammation, but only confirms suspicion.To detect bacterial prostatitis, laboratory examinations can be performed
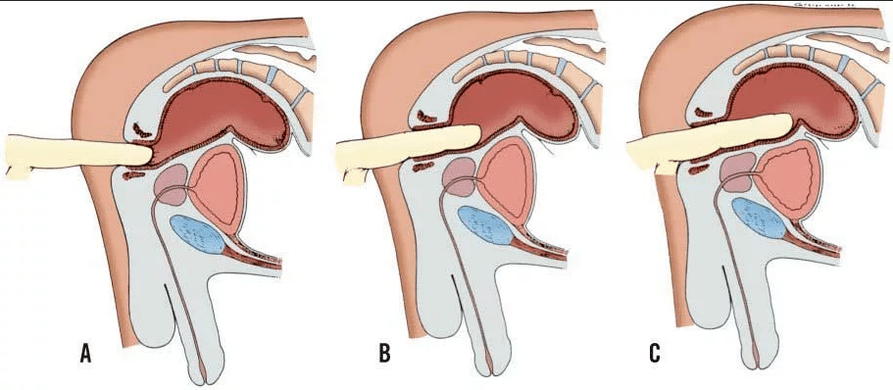
Finger's rectal examination
Because the prostate gland borders directly with the rectum, it can be felt in the rectum.These digital rectal studies are conducted in outpatients and without anesthesia, usually without pain.The patient is asked to lie down with a crooked leg.Using the lubricant, the doctor slowly inserted the finger into the anus and scan the prostate organs and adjacent.He studies the size and sensitivity of pain in the prostate gland.
Laboratory
To identify possible pathogens in most cases, urine analysis is performed.The standard method is a sample called four glasses.Here Erturin, Mittelstrahlurin, ProstataExPlike and urine are tested after the prostate massage.As called prostataxprims, doctors call the prostate secretion.This is achieved by a doctor by mild pressure on the prostate, for example, on palpation.Ejaculate can also be tested for pathogenic microorganisms and signs of inflammation.
Further research
Rectal ultrasound scanning can be used to determine exactly where the inflammation is and how far it is spread.An important goal of this study is also an exemption of other diseases with the same symptoms.
To exclude that the existing urine drainage violation is due to the narrowing of the urethra, the urine flow is measured.The usual flow of urine is from 15 to 50 milliliters per second, while urine flow is ten milliliters per second or less, there is a high probability of urethra obstruction.
Prostatitis: Treatment

Drug therapy
Acute bacterial prostatitis is treated with antibiotics.In light cases, the dose of antibiotics is sufficient for ten days.In chronic prostatitis, the drug should be taken for a longer period of time.Depending on the pathogenic microorganisms, the active ingredients of luxacin, ciprofloxacin, azithromycin, erythromycin or doxycycline.Although the symptoms have declined, antibiotics under any circumstances should be continued according to the appointment of a doctor.
Also, asymptomatic prostatitis is treated with antibiotics.
In the event of chronic abacterial prostatitis, antibacterial therapy is usually ineffective.With chronic pelvic pain syndrome, despite lack of evidence of pathogen presence, studies are conducted using antibiotics, as sometimes improvements can be achieved.However, with non -inflammatory syndrome chronic pelvic pain, antibiotic therapy is not recommended.
Another therapeutic approach to chronic abacterial prostatitis is a 5α-reductase inhibitors called, such as fineride or dutasteride, polyisulphate and plant drugs, such as quercetin or dust extract.If the increase is not achieved, drug therapy will be supplemented by physiotherapy.Here, physiotherapy exercises, exercises for pelvic floor muscles or ordinary prostate sequences are recommended.
In addition, symptom therapy can help relieve acute symptoms of prostate infection.Anesthetic medications can be prescribed for severe pain.Also, heating pads and heating pads on the back or lower abdomen help to relax the muscles.This often relieves pain with prostate inflammation.
Recurrence
The frequency of prostatitis relapse is generally very high.About 23 percent of the victims are subject to the second episode of the disease after one disease, 14 percent suffer from three, and 20 percent - even from four or more cases of disease.To reduce recurrent risk, avoid wearing wet clothing during or after prostatitis, hypothermia or bubble use, such as black tea or coffee.This reduces the risk of cystitis and, therefore, prostatitis.However, you cannot prevent bacterial prostatitis using this method.
The prognosis of prostatitis depends, on the one hand, on the cause of inflammation, and on the other hand, how quickly the correct therapy begins.
In acute bacterial prostatitis, which is treated as soon as possible with antibiotic therapy, prognosis is usually good.Taking antibiotics, dead pathogens, which usually prevent the transition to chronic prostatitis.
About 60 percent of all patients with acute prostatitis no longer have symptoms in six months, and about 20 percent develop chronic prostatitis.Treatment and prognosis are more difficult here.In many cases, periodic episodes of the disease can accompany those who suffer for years.
Chronic prostatitis usually requires great patience from the victim.Often long courses can be a serious psychological burden.
Patients who have suffered should seek professional help, as mental health has a significant impact on prostatitis predictions.